Munitions / Air to air missiles / K-13 (NATO: AA-2 Atoll)
K-13 (NATO: AA-2 Atoll)
General Facts
- TYPE
Air to air missile - ORIGIN
 USSR
USSR - NICKNAMES
AA-2 Atoll (NATO reporting name)
A-91 (Romanian production) - DESIGNED
1958 - 1960 (R-3)
1960 - 1961 (R-3S)
1960 - 19 - DESIGNER
Turopov OKB-134 design bureau - PRODUCTION
1962 - ? (R-3S)
1966 - ? (R-3R)
1974 - ? (R-13M) - PRODUCERS
 Romania
Romania
 USSR - Vympel
USSR - Vympel - QUANTITY
Ten thousands - UNIT COST
Unknown - CHARACTERISTICS
 Better performance than AA-1
Better performance than AA-1
 Low production costs
Low production costs
 Usable on many aircraft
Usable on many aircraft
 Tail engagement only
Tail engagement only
 Limited range
Limited range
 Vulnerable to countermeasures
Vulnerable to countermeasures
 Lengthy lock on time
Lengthy lock on time
Introduction
The K-13 is an air to air missile of Soviet origin. It was a direct copy of the US AIM-9B Sidewinder air to air missile and introduced in Soviet service in the early 1960's. In the West the K-13 is better known by its NATO reporting name AA-2 Atoll. The USSR came into possession of an AIM-9B which was lodged in the tail of a Chinese MiG-17 but did not explode.
Layout
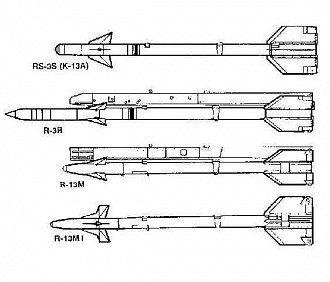
The early versions of the K-13 were a direct copy of the AIM-9B. It was copied in such detail that parts were interchangeable. Improved versions were later developed by the USSR. The K-13 is a infrared guided missile with four large wings at the rear and four smaller ones at the front. The guidance section is located at the front, the warhead in the middle and the rear half is made up of the solid propellant rocket motor.
Guidance
The original version of the K-13 is the R-3S with an uncooled infrared seeker and restricts it as a tail chase missile. The much improved R-13M has a cooled infrared seeker with a much better performance but it remains a tail chase missile. The R-3R has semi-active radar homing and has an all aspect engagement capability. The radar seeker operates in the J-band and is compatible with radars such as used in the MiG-21 Fishbed.
Firepower
The K-13 was a vast improvement over the earlier AA-1 Alkali. The R-3S has a maximum range of 7 km and the improved R-13M may reach out to 15 km. However, since both missiles are tail chase only the range against a target with a similar speed as the launch aircraft is only 2 and 3 km respectively.
Platforms
The K-13 may be used by a wide variety of Soviet aircraft. Many aircraft that use more capable missiles in Soviet service were fitted with the K-13 in export models. The original K-13 models are used on the MiG-19, Yak-25 and early versions of the MiG-21, MiG-23 and Su-17. The R-13M is often used on the late versions of the MiG-21, MiG-23 and Su-17, as well as on the Su-25 and other newer Soviet aircraft.
Users
The K-13 was one of the most widely exported air to air missiles in the world. During the Cold War it was used by most Soviet and Warsaw Pact aircraft and exported to most Soviet allies during the Cold War. Nowadays it is considered obsolete and has been fully replaced with more modern air to air missiles in most nations. However, it remains in widespread second line use with many nations as a weapon that arms older types of fighters and ground attack aircraft.
R-3S
The original R-3 and R-3S are direct copies of the AIM-9B Sidewinder and many parts are interchangeable with the AIM-9B.
R-3: Original direct copy of AIM-9B introduced in 1960 with 11 second lock on time. System known as K-13.
R-3S: First production version of R-3 which was introduced in 1962. It includes some Soviet components resulting in 22 second lock on time. System known as K-13A, NATO name AA-2A Atoll.
R-3U: Captive training missile to train pilots on homing system.
R-3P: Fully functioning R-3S without warhead for training.
RM-3V: R-3S converted to aerial target.
- Specifications:
- R-3S
| Type | Air to air missile |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 127 mm body, 528 mm wingspan |
| Length | 2.838 mm |
| Weight | 75.3 kg |
| Guidance | Infrared homing, uncooled |
|---|---|
| Warhead | 11.3 kg HE-frag |
| Propulsion | DWP-80A single stage solid propellant rocket motor |
| Speed | 550 m/s max |
| Range | 0.9 to 7 km max, 2 km effective |
|---|---|
| Altitude | - |
| Engagement envelope | Tail aspect only, 50 m to 21.5 km altitude, up to 3 G maneuvres |
| Remarks | - |
R-3R
The R-3R is the semi-active radar homing version of R-3S which is longer and has all aspect engagement ability. The entire system is known as K-13R and the NATO name is AA-2C Atoll. The development started together with the R-3S but the development took longer and the missile was introduced in 1966.
- Specifications:
- R-3R
| Type | Air to air missile |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 127 mm body, 528 mm wingspan |
| Length | 3.417 mm |
| Weight | 83.5 kg |
| Guidance | Semi-active radar homing |
|---|---|
| Warhead | 11.3 kg HE-frag |
| Propulsion | DWP-80A single stage solid propellant rocket motor |
| Speed | 550 m/s max |
| Range | 1.5 to 8 km |
|---|---|
| Altitude | - |
| Engagement envelope | All aspect, 1 to 20 km altitude, up to 2 G maneuvres |
| Remarks | - |
R-13M
The R-13M is a much improved version of the R-3S and has capabilities similar to the AIM-9G Sidewinder. The R-13M is still a tail engagement missile only but is far more capable than the R-3S due to its new seeker and rocket motor. The new cooled seeker is more accurate and somewhat more resistant to countermeasures. The new rocket motor burns longer The redesigned body makes the R-13M more maneuverable. The system is known as R-13M and the NATO designation is AA-2D Advanced Atoll. The designation AA-2-2 is sometimes used as well.
R-13M: Original version introduced in 1974.
R-13M1: Improved R-13M with new forward fins introduced in 1976.
| Type | Air to air missile |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 127 mm body, 632 mm wingspan |
| Length | 2.875 mm |
| Weight | 87.7 kg |
| Guidance | Infrared homing, cooled |
|---|---|
| Warhead | 11.3 kg HE-frag |
| Propulsion | DWP-240 single stage solid propellant rocket motor |
| Speed | 550 m/s max |
| Range | 0.9 to 15 km max, 3 km effective |
|---|---|
| Altitude | - |
| Engagement envelope | Tail aspect only, 50 m to 21 km altitude, up to 7 G maneuvres |
| Remarks | - |
| Type | Air to air missile |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 127 mm body, 651 mm wingspan |
| Length | 2.876 mm |
| Weight | 90.6 kg |
| Guidance | Infrared homing, cooled |
|---|---|
| Warhead | 11.3 kg HE-frag |
| Propulsion | DWP-240 single stage solid propellant rocket motor |
| Speed | 550 m/s max |
| Range | 0.3 to 17 km max, 3 km effective |
|---|---|
| Altitude | - |
| Engagement envelope | Tail aspect only, 50 m to 25 km altitude, up to 8 G maneuvres |
| Remarks | - |