Project 183 Bolshevik class
NATO: P-6 class
Overview

P-6 class
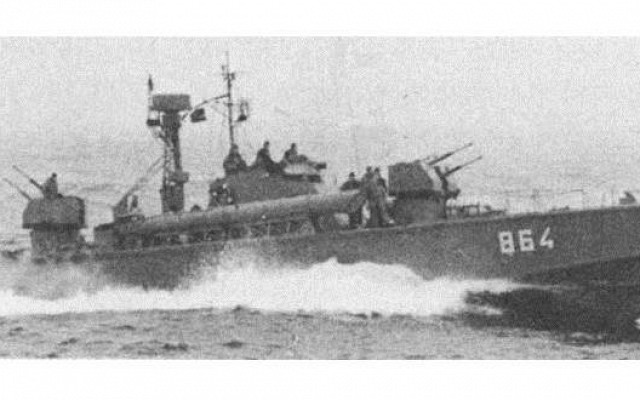
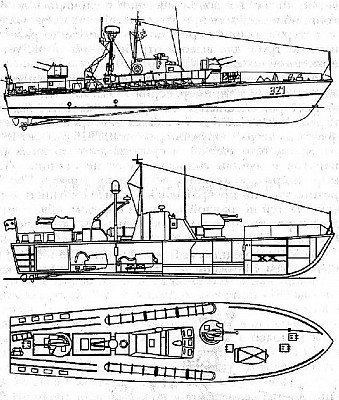
East German P-6 class with depth charges clearly visible behind torpedo tubes.
Source: www.harpoondatabases.com -
© copyright lies with original owner
1958 - 1966 (China)
Soviet Union - No. 602 shipyard, Vladivostok
Soviet Union - No. 640 shipyard, Sosnovka
China
North Korea
26 Project 183T/TK
60 Project 183 Ts
At least dozens in China
At least 40 in North Korea
P-6 class (NATO reporting name)
China
North Korea
Egypt
Description
Introduction
The P-6 class is a motor torpedo boat of Soviet origin. It was developed in the early 1950's to complement the older and smaller P-4 class. These motor torpedo boats were used in large numbers from shore bases and were intended to intercept incoming enemy frigates and destroyers. The P-6 class was widely used by Soviet forces during the early decades of the Cold War but is obsolete nowadays. The hull of the P-6 class was later used in the Komar class which carried anti-ship missiles instead of torpedoes. In China the Swatow (Type 55A Shantou) class gunboat was developed on the P-6 hull.
Layout
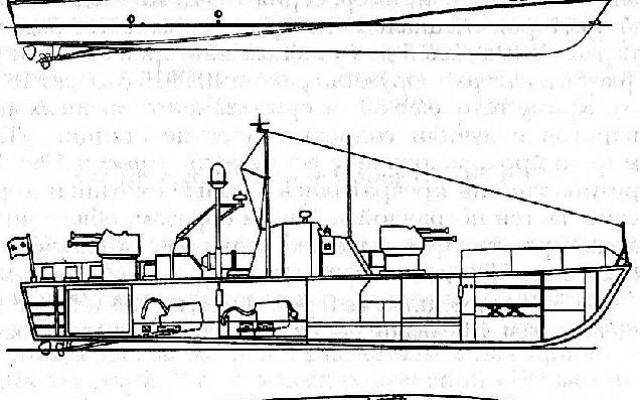
The P-6 is a much larger vessel than the earlier P-4 and has better sea going ability. The P-6 has a classic motor torpedo layout with a small cabine in the middle, the engines at the rear and the torpedo tubes at each side of the cabin. A small gun turret is located in front of and behind the cabin. The hull was made of a treated plywood sandwich to keep the weight down. A retractable radar mast is fitted for navigation and surface search.
Firepower
The P-6 is armed with two 533mm torpedo tubes that launch the Type 53 series of torpedo. The P-6 is usually fitted with World War 2 era straight running torpedoes, although some early Cold War designs can also be used. Instead of torpedoes two mines can be carried. There are also simple side mounted racks for up to 12 depth charges. On the front deck and the aft deck a turret with two 25mm 2M3 autocannon are fitted. These guns can be used against aircraft and surface targets and are manually aimed.
Mobility
The P-6 has four diesel engines that are directly connected to a single shaft with a fixed pitch propeller. The engines cannot be set to reverse which hampers maneuvering in confined spaces. The diesel engines can lay a smoke screen by injecting fuel in the exhaust. The maximum speed is 43 knots. When travelling at 30 knots the operational range is 450 nm.
Users
The P-6 class is one of the most produced military vessels in the world totaling over 600 ships. Large quantities were used by the USSR navy and exported to various allies, some of which also produced them under license. With the introduction of missile armed attack craft the motor torpedo boat became obsolete and most were scrapped in the 1970's and 80's. Only Egypt has a number of modified vessels in active use.
Variants

P-6 class
Forward view of P-6 with sensor mast lowered.
Source: www.harpoondatabases.com -
© copyright lies with original owner
Details
Media
Subcomponents
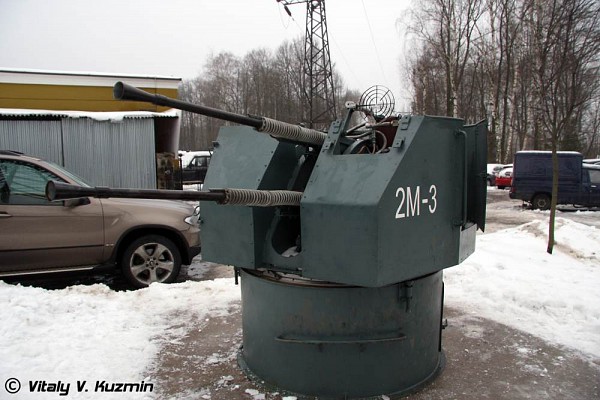

25mm 2M-3
Two 2M-3 turrets with two 25mm autocannon each are fitted to the Project 183 Bolshevik class. These can be used against aerial and surface targets. Since these are manually operated their anti-aircraft effectiveness is limited.
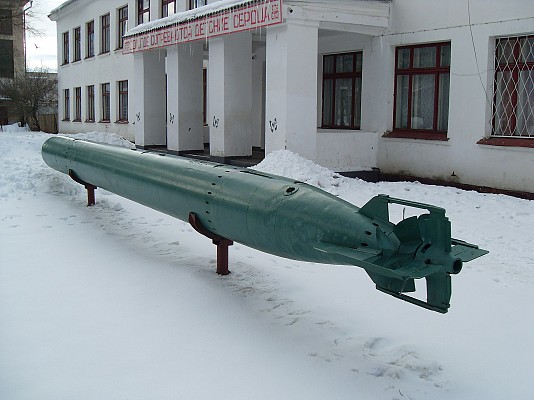

Type 53-38
One of the types of 533mm torpedoes used by the Project 183 Bolshevik class is the World War 2 era Type 53-38U heavyweight torpedo.
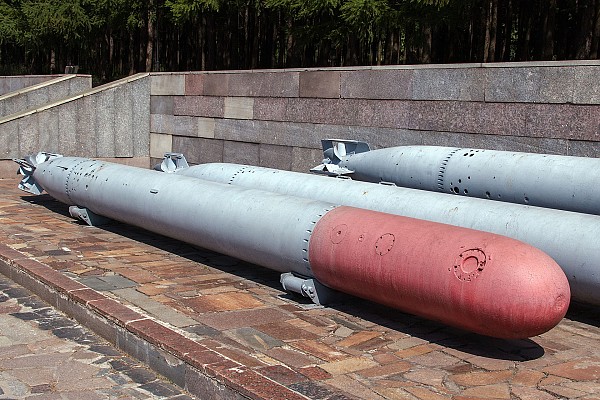

Type 53-39
The Type 53-39 was often used on the Project 183 Bolshevik motor torpedo boats.
Related articles

Project 183R class
The Project 183R (NATO: Komar) class missile boat is based on the design of the Project 183 torpedo boat.

Type-055A Shantou class
Chinese gun boat based on the Project 183 hull design. Made of steel and armed with gun armament instead.