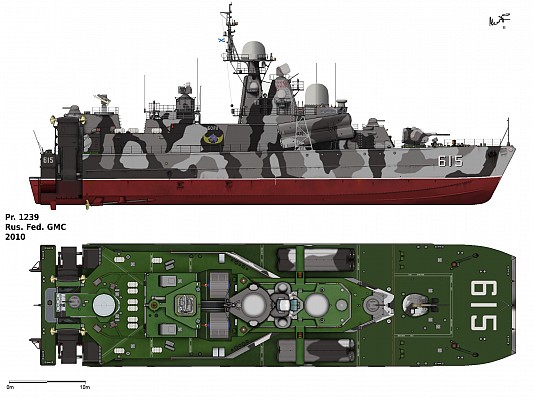
Project 1239 Sivuch class
NATO: Dergach class
Overview
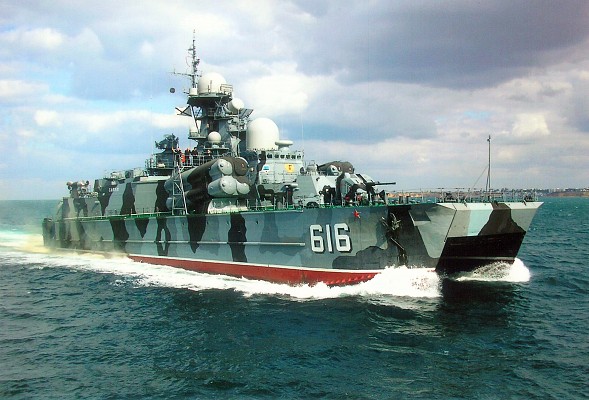

Project 1239 class
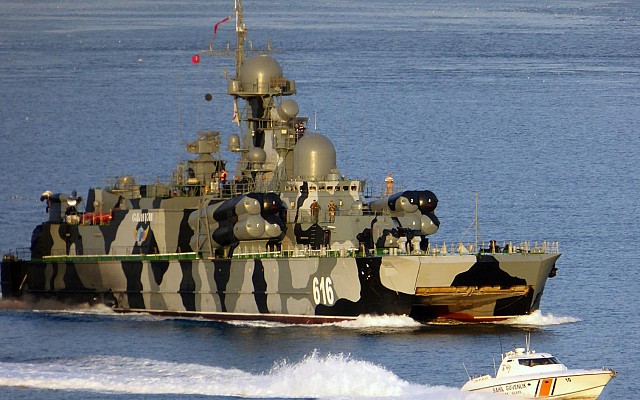
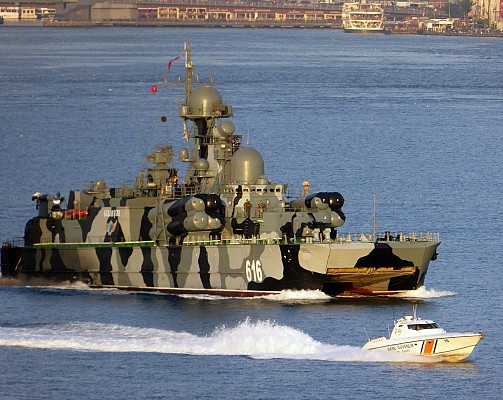
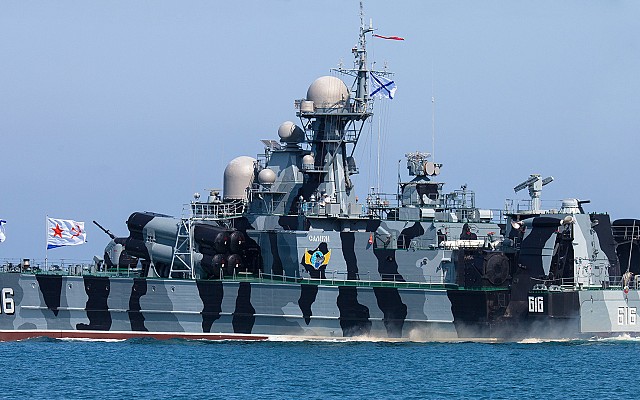
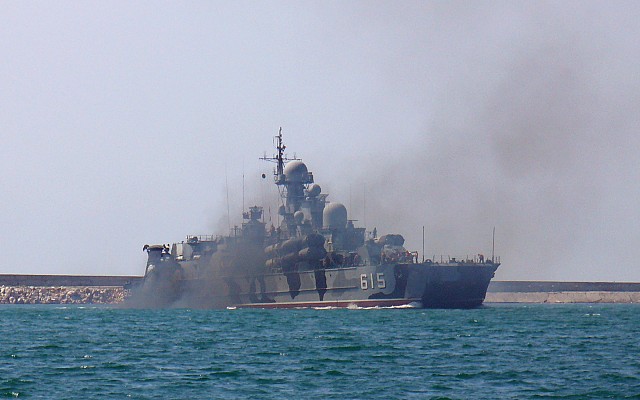
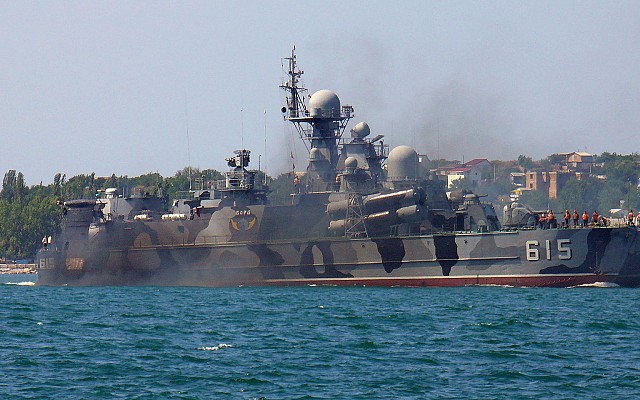
Russian navy Project 1239 (NATO: Dergach) class guided missile corvette.
Source: Unknown author -
© Copyright lies with original owner
Dergach class (NATO reporting name)
Sivuch (lead ship)
Bora (lead ship, renamed)
Russia
Description
Introduction
Project 1239 Sivuch is a late Cold War era guided missile corvette of Soviet origin. This class is known in the West under the NATO reporting name Dergach class. Project 1239 is of a very unique design combining the features of a catamaran, a hydrofoil and hovercraft. The goal of this unique setup was to create a very fast guided missile corvette. Despite being the first design to use this unique setup the Project 1239 proved to be a functional, quite reliable and seaworthy design. Still, the slight increase in effective speed was not deemed worth the complexity of this design.
Design
Project 1239 uses a catamaran hull design with the three types of engine lined up in the two floats to lower the point of gravity. In transit mode this ship uses its two diesel engines each directly connected to a single shaft. For movement at high speed two hydrofoil wings are lowered. These feature two screws each in a push-pull configuration and are powered by the gas turbines. The front of the ships is lifted an air cushion inflated by two dedicated diesel engines. This unique propulsion system also comes at a cost. Project 1239 has twice the displacement of a Project 1241.1M Molniya (NATO: Tarantul III) class missile boat, while both ships have a similar superstructure, sensor package and weapons suite. With a practical maximum speed of 41 knots the Molniya isn't much slower than the sustained 45 knots speed of Project 1239.
Sensors
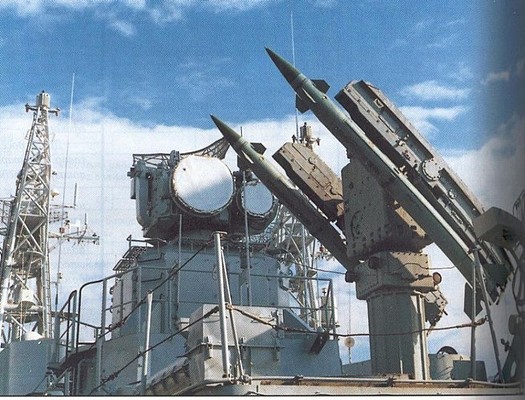
The sensor suite is possibly one of the most advanced ever put on an air cushion vehicle. The 34K1 Monolit surface search radar is used to detect surface targets for the highly capable Moskit supersonic anti-ship missiles. The MR-352 Pozitiv air search radar provides a 3D picture and is used as input for the Osa-MA2 SAM system and the dual purpose gun armament. There is no sonar system. Self-defense consists of an electronic surveillance and warfare suite and a several types of chaff and flare dispensers.
Firepower
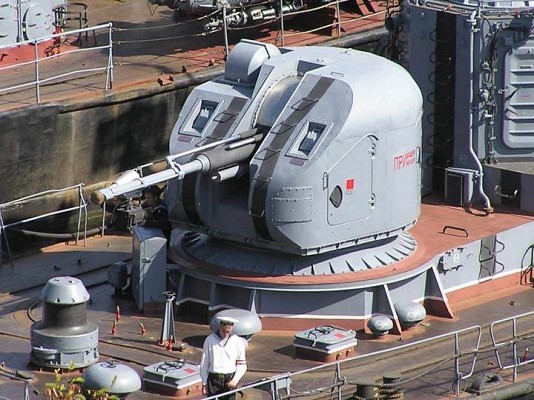
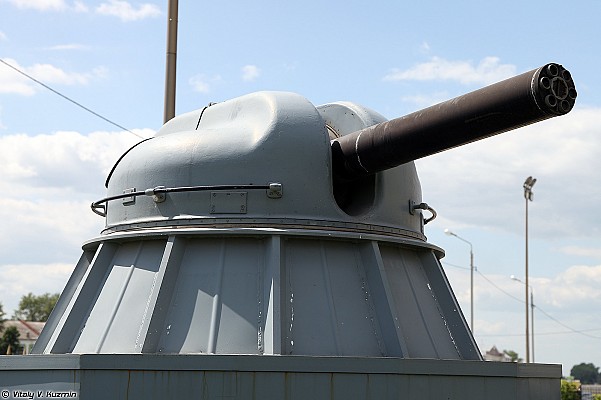
The Moskit supersonic anti-ship missile is the main anti-shipping armament. Eight of these highly capable missiles are carried and ready to launch. A 76mm AK-176M dual purpose gun can also be used against surface targets. Short range air defense is provided by the Osa-MA2 surface to air missile system. Two 30mm AK-630M close-in weapon systems and man portable SAM systems provide point defense. The is no anti-submarine armament.
Mobility
Mobility is the key feature of the Project 1239. When using both the hydrofoils and the air cushion a maximum speed of nearly 53 knots can be achieved. In operational service a speed of just below 50 knots is said to be attainable for a longer duration. Reportedly Project 1239 is a stable platform at sea and quite reliable despite having three types of engines. The main reason is probably that there are no transfer cases combining the power of multiple engines, all are individually connected to the shafts.
Users
Project 1239 was produced in limited numbers. One was commissioned in 1989 just before the fall of the Soviet Union. The second was was launched in 1992 but not completed until the year 2000. The third was in the preliminary phase of construction before cancellation in the 1990's. Both ships were renamed and remain in active service with the Russian navy, being part of the Black Sea fleet.
Media
Details
Subcomponents
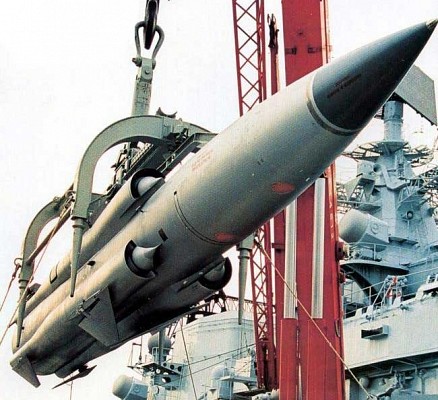

P-270 Moskit
2x4 KT-190 launchers for Moskit supersonic anti-ship missile.