9K115 Metis
NATO: AT-7 Saxhorn
Overview
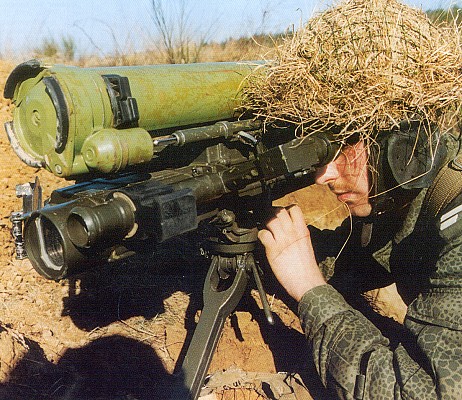

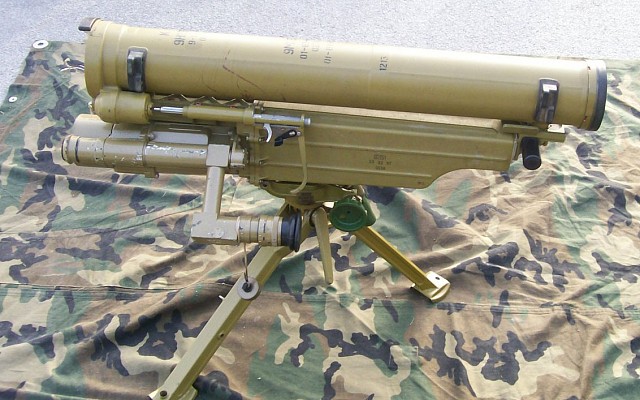
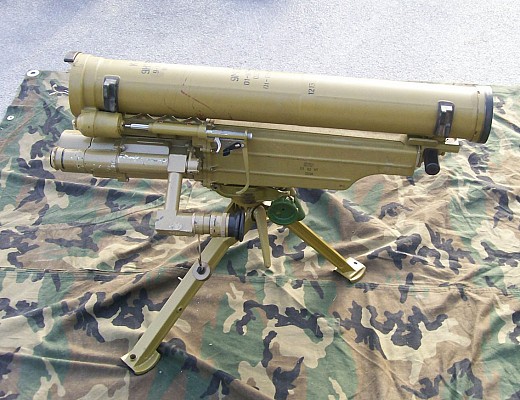
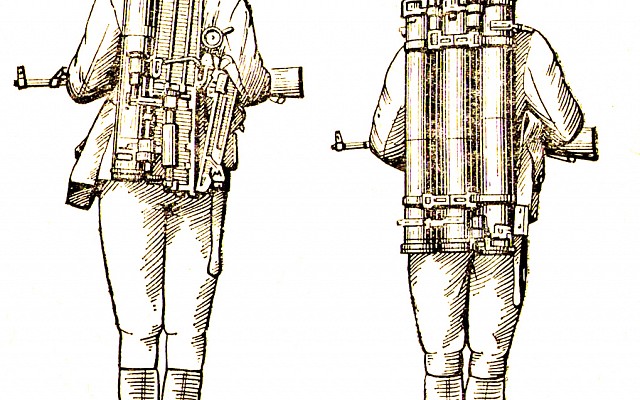
9K115 Metis
9K115 Metis in Polish service.
Source: Ministerstwo Obrony Narodowej -
© GNU Attribution Share Alike license
9K115 (GRAU index for entire system)
9M131 (GRAU index for missile)
9P151 (GRAU index for launch post)
Description
Introduction
The 9K115 Metis is a late Cold War era man portable anti-tank missile system of Soviet origin. It was developed as a more mobile alternative to the 9K111 Fagot (NATO: AT-4 Spigot). In the West the 9K115 system is better known by the NATO reporting name AT-7 Saxhorn. The 9K115 is often considered the Soviet counterpart of the M47 Dragon. Shortly after the collapse of the USSR the 9K115-2 Metis-M was introduced. This is an improved system with newer and more capable missiles.
Design
The 9K115 system consists of the 9P151 tripod mounted launcher with 9S816 sight module and the 9M115 anti-tank missile. The missile is wire guided and features SACLOS guidance. The launcher is reusable. The 9K115 system itself is operated by a single person. A regular crew consists of three people who carry five missiles in total.
Firepower
The 9M115 missile features a single HEAT warhead that can penetrate 460 mm RHA. This makes it effective against all types of combat vehicles, except for use against contemporary and modern tanks over the frontal arc. The maximum range of 1 km is rather limited. However, the minimum range of 40 meters makes the 9K115 well suited for urban combat use. The 9K115 can also be fired from inside structures, albeit from large rooms only.
Mobility
The 9K115 is a very portable system. It is one of the few guided anti-tank missile systems that can be effectively used by a single soldier. Aside from urban combat this makes the 9K115 also suitable for use by mountain and airborne troops. Apparently the 9K115 can be fired from the shoulder as well.
Users
The 9K115 was tested from 1978 onwards and adopted with Soviet forces in 1982. Although it was indeed lightweight and suitable for urban combat, its effectiveness was deemed limited. The 9K115 was adopted and exported in limited numbers compared to other Soviet anti-tank missile systems. The improved 9K115-2 Metis-M replaced the 9K115 in production in the early 1990's. This new design improved upon the two major shortcomings: maximum range and armor penetration.
Media
Details
Related articles
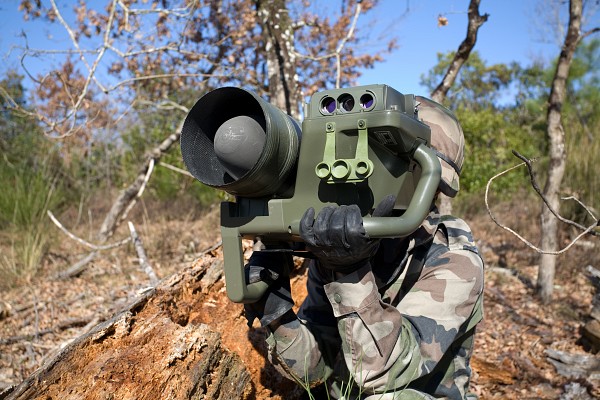

Eryx
The French Eryx is somewhat similar to the 9K115 Metis. Both systems are highly portable guided missiles with a very short range.
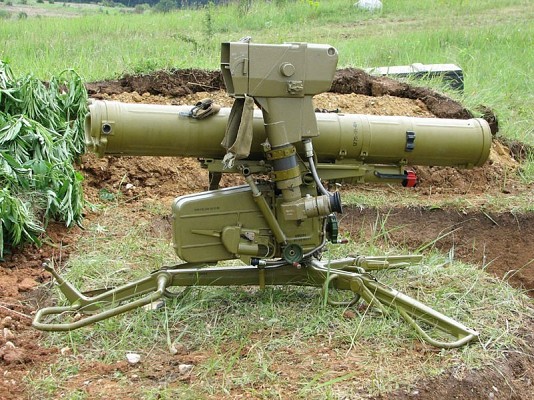

9K111 Fagot
The 9K115 Fagot was produced in limited numbers, since the more powerful and longer range 9K111 Fagot (NATO: AT-4 Spigot) proved portable enough for most applications.