Bofors M/50
Creusot-Loire Modèle 54 | Mitsubishi Type 71
Overview

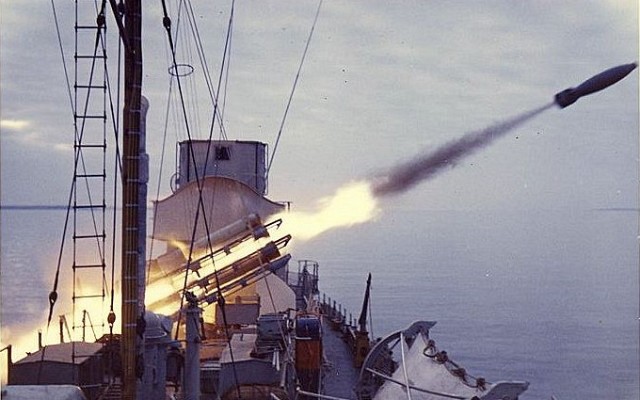
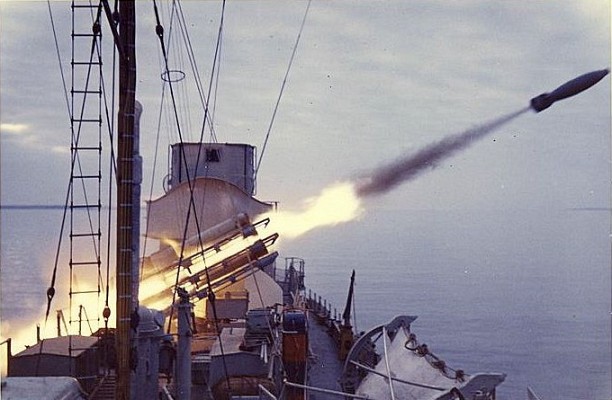
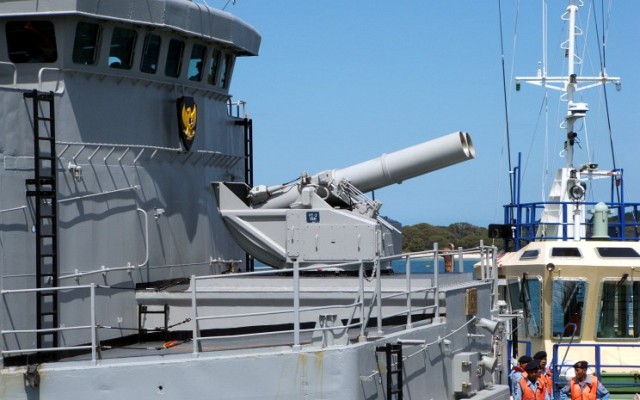
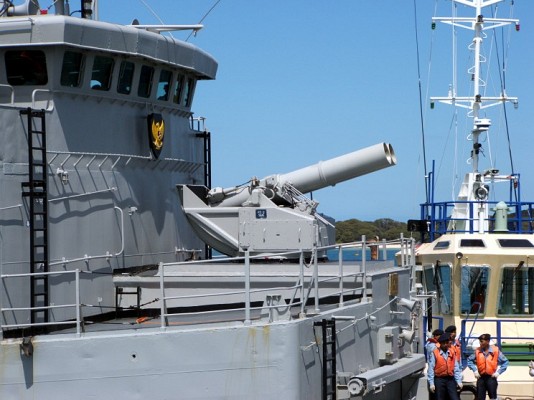
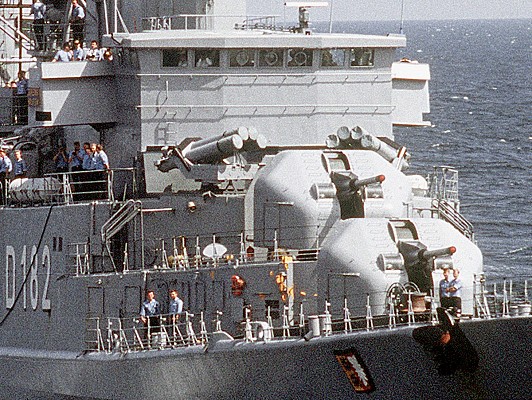
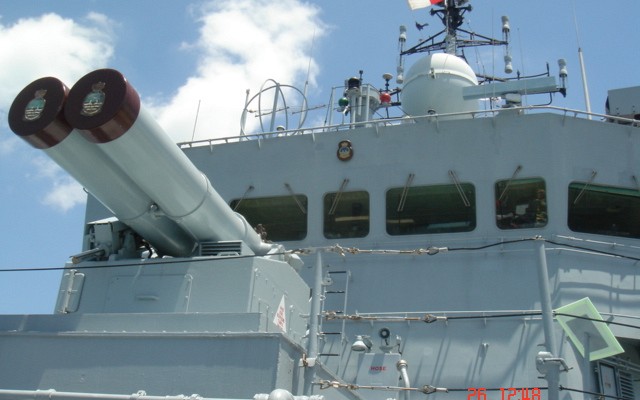
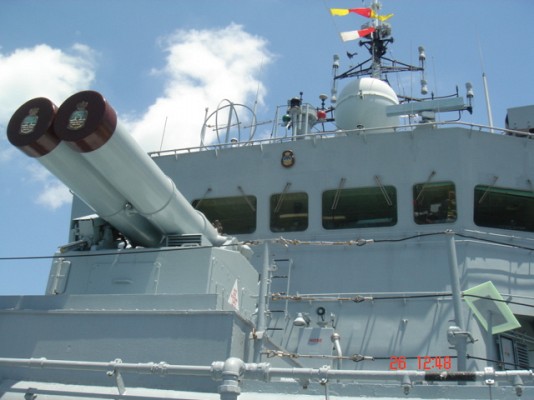
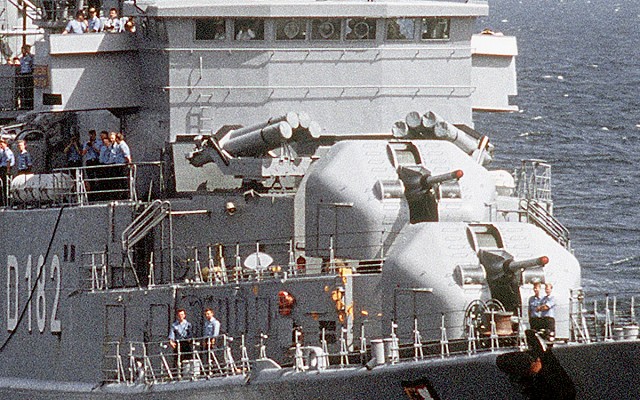
Bofors B4 launcher
Two Bofors B4 quadruple launchers for 375mm rockets on a Halland class destroyer.
Source: Marcusroos -
© GNU Attribution Share Alike license
France - Creusot-Loire
Japan - Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
SR-375A (alternative name for Bofors B2)
Netherlands
France
Japan
Germany
Description
Introduction
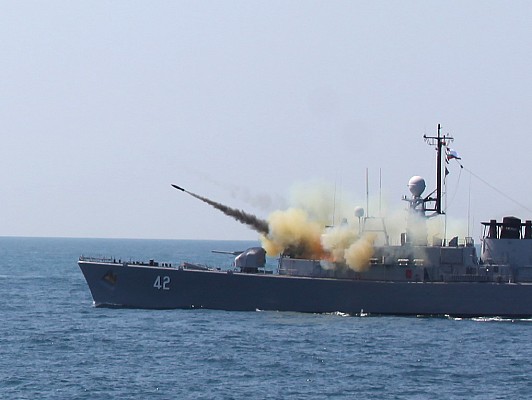
The Bofors M/50 is a naval anti-submarine warfare rocket depth charge system of Swedish origin. It was developed after World War 2 and entered service in the early 1950's. Several types of launchers and and a selection of 375mm rockets were developed over time. During the Cold War the Bofors M/50 was used in many European ships and was exported to various nations. Although over the last decades usage has declined in favor of lightweight torpedoes, many of these systems remain in service today.
Design
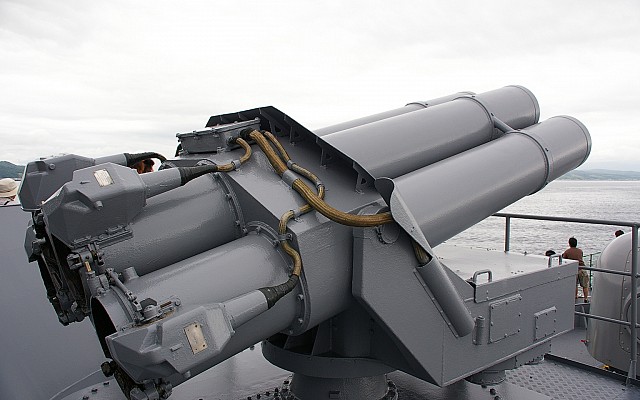
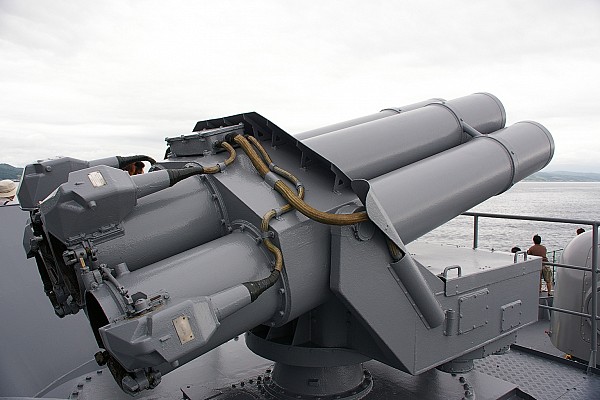
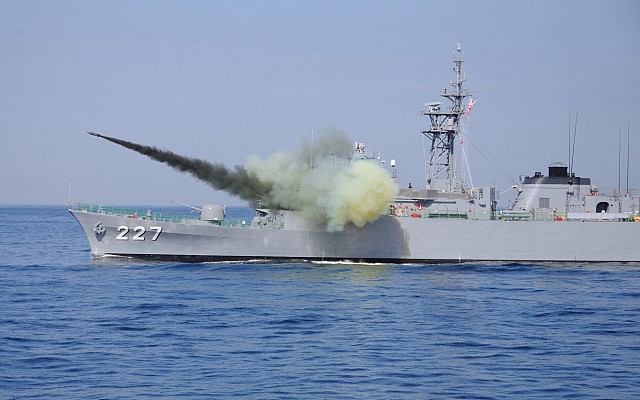
The Bofors M/50 was one of the first operational anti-submarine depth charge systems combining accurate fire control using sonar input and rocket powered depth charges. Over time the launchers, fire control systems and ammunition were continuously improved. The general layout of these systems is identical. The unmanned multi-barrel launcher is the visible component of the system. Underneath the launcher there is an ammunition handling room. In the reloading position the barrels are raised and loaded from the rear.
Fire control
All Bofors M/50 launchers are unmanned and use a fire control systems. Early models introduced in the 1950's used and electro-mechanical predictor. Later at least four types of digital fire control systems were developed in Sweden and abroad. In all cases sonar input is used to determine traverse, range and depth. Range is controlled by elevation of the launcher in combination with the weight and velocity of the selected ammunition type.
Firepower
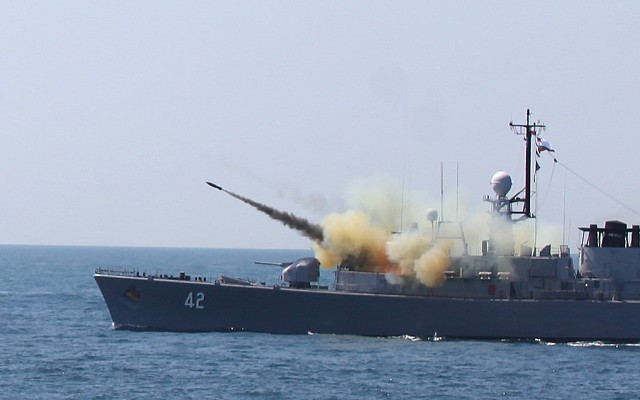
Several types of 375mm rockets can be used in the Bofors M/50. Most have a warhead with over 100 kg of explosive filler. Early rocket had a measly 0.8 km range, which was doubled in the Erika, the most common type of rocket. Early rocket types used impact and time fuses. The Nelli rocket introduced in the 1970's introduced a proximity fuse. The Nelli also has a longer 3.6 km range and a lighter 80 kg warhead.
Users
The Bofors M/50 was first acquired by Sweden and the Netherlands, both using the quadruple B4 launcher on their detroyers. France developed the six tube variant in the 1960's and used it in various classes of frigates. In the early 1970's Japan acquired a local production license and used the B4 launcher on various classes of frigates. The introduction of the lightweight B2 launcher allows installation on corvettes and smaller frigates, leading to various export sales around the world.
Variants
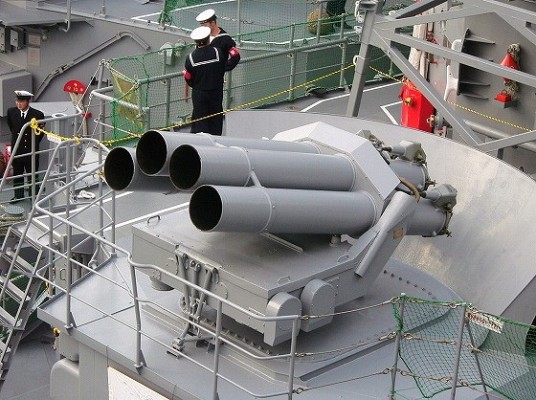

Bofors B4
Quadruple launcher introduced by Bofors in 1956. Known as M/50 at first and later designated B4. Produced under license in Japan as the Type 71. Nominal ammunition storage is 48 rockets per launcher. The semi-automatic loading system loads one round at a time, with four tubes being reloaded in 3 minutes.
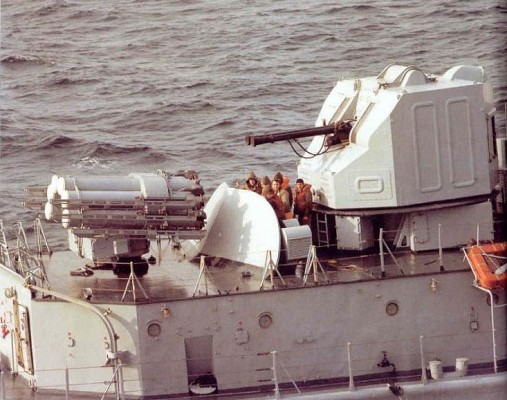

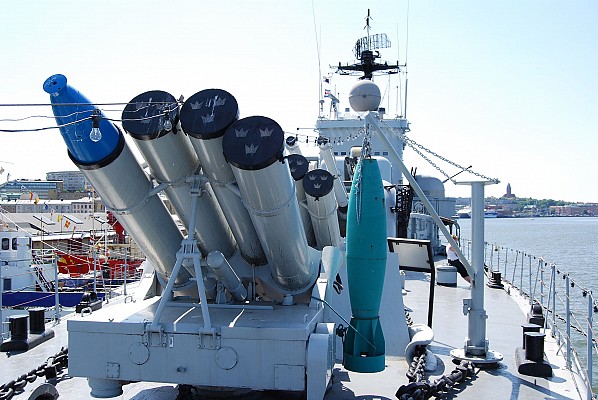
Modèle 54
Sextuple launcher developed by French company Creusot-Loire, first introduced in 1967. The sextuple launcher was designed to approximate the firepower of two quadruple B4 launchers in a single mount. Ammunition varies per class and is between 30 and 72 rockets.
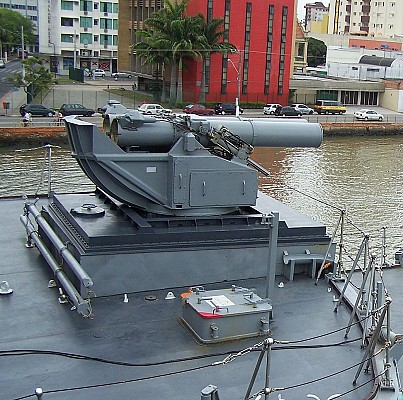

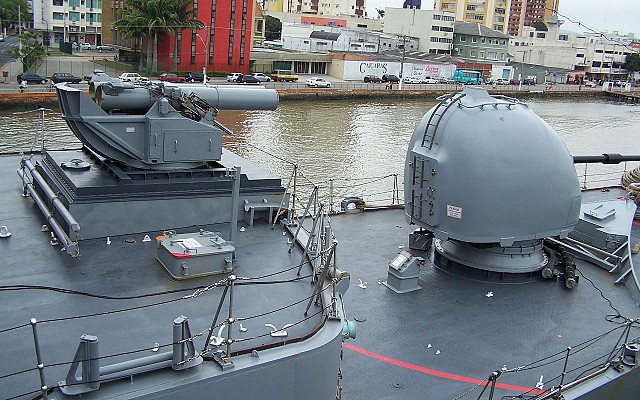
Bofors B2
Twin launcher introduced by Bofors in 1972. Most compact version of the launchers, while not sacrificing effective firepower. This is achieved by an improved reloading system that loads two rounds simultaneously in 30 seconds.
Details
Ammunition types
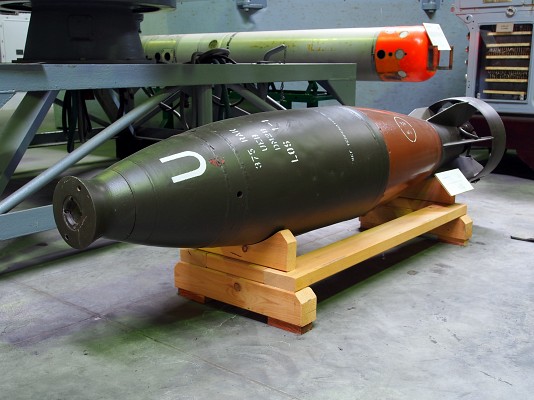

Bofors 375mm M/50
The Bofors M/50 series of launchers can fire several ammunition types. These are described in a seperate article.