9M311
NATO: SA-19 Grison
Overview

9M311
Side view of a 9M311 series missile with booster section (black) attached to the missile section (white).
Source: pvo.guns.ru -
© Copyright lies with original owner
Russia
SA-N-11 (NATO reporting name for naval use)
9M87 / 9M88 (GRAU index)
Russia
India
Description
Introduction
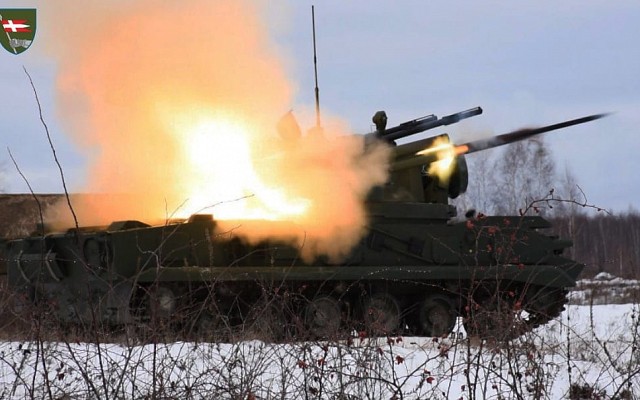
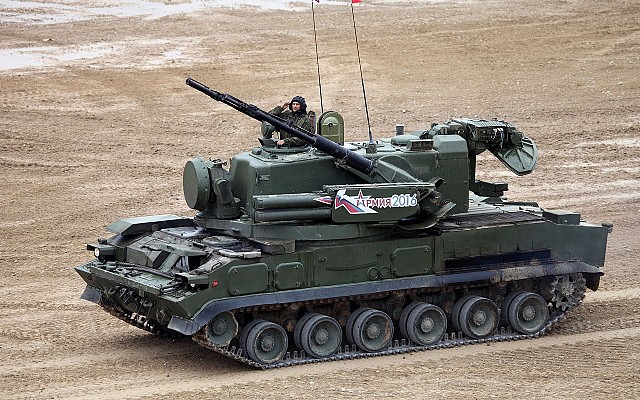
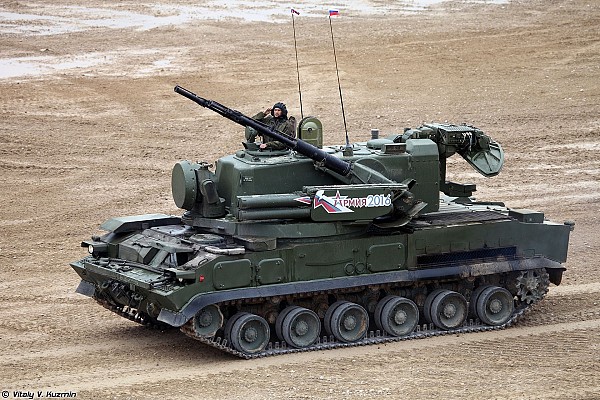
The 9M311 is a late Cold War era surface to air missile of Soviet origin. It was developed in the late 1970's for use on the Tunguska self-propelled anti-aircraft gun and SAM system. The NATO reporting name is SA-19 Grison.
Design
The 9M311 missile is a two stage missile that is transported and launched from a long cylindrical launch tube. Upon launch a gas ejector pushes the missile from the launch tube and a large diameter solid propellant booster ignites immediately thereafter. This pushes the missile to a maximum speed of over 900 m/s in less than 3 seconds. At this range of about 2.4 km the booster detached and the smaller diameter guided missile section continues the flight towards the target. A combination of impact and proximity fuses detonates the warhead.
Guidance
Radio command guidance is used to guide the missiles onto target. Two lights on the missile indicate its position. An electro-optical tracker on the launch vehicle or ship determines the position of the missile in relation to the target tracked by the tracking radar. A central fire control computer determines course corrections and these are passed on to the missile in flight by radio commands. The onboard computer in the missile translates these commands into movement of the control surfaces. There is a back-up guidance mode in which the gunner uses a stabilized sight to track the target.
Firepower
The 9M311 has a maximum range of 8 km in the earlier missile types and 10 km in the latest variant. The missile has a maximum speed of 900 m/s and average speed of about 600 m/s. Minimum engagement range is about 1.3 km. The altitude envelope ranges from 15 m up to 3.5 km.
Platforms
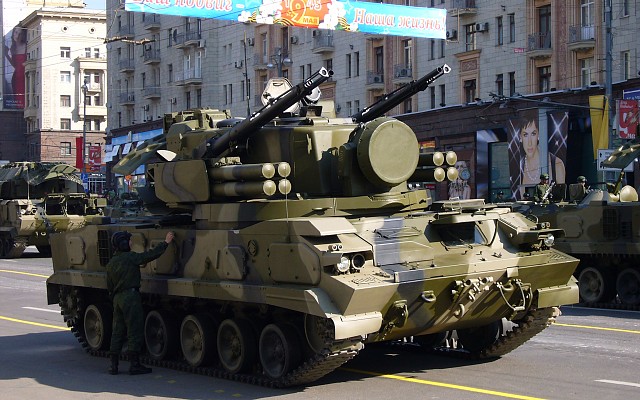
9M311 was introduced in 1982 on the 2S6 Tunguska self-propelled anti-aircraft gun and SAM system. This was followed by the Kortik naval SAM system in the late 1980's. The missile design was updated twice and two export versions exist. Early on a specific naval variant of the 9M311 exists, although these seem to be unified in the final 9M311M1 variant.
Users
The first and most prolific user of the 9M311 was the Soviet Union, with most 2S6 Tunguska and naval vessels with Kortik ending up in Russian service, although a sizeable number ended up in Ukrainian service. India is the major export user of the 2S6 Tunguska. The Kortik/Kashtan system is also in use with China.
Variants
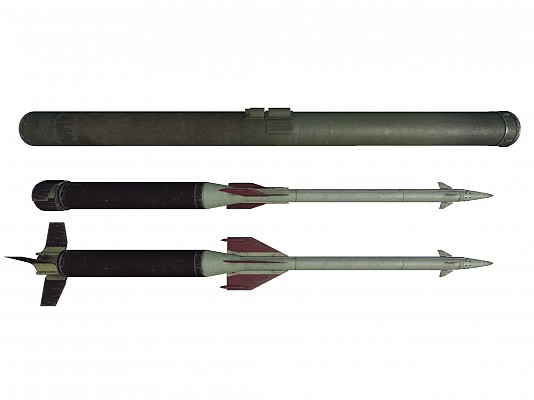

9M311 missile
Digital artist impression of 9M311 cannister (top) with missile with wings in folded (center) and extended (bottom) position.
Source: Flame2512 @ wiki.warthunder.com -
© Copyright lies with original owner
List of 9M311 missile variants
Details
Media
Platforms
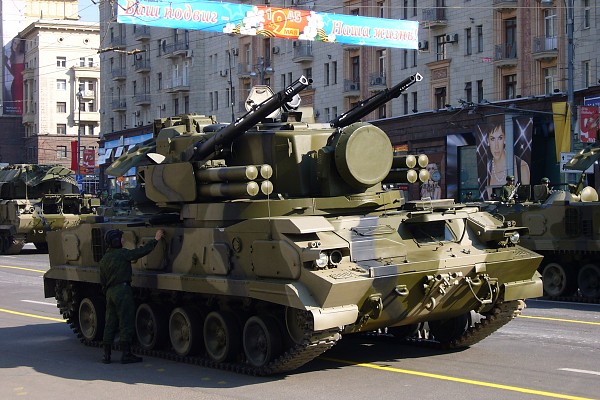

2S6 Tunguska
Eight 9M311 missiles are ready to fire on the 2S6 Tunguska, a tracked self-propelled anti-aircraft gun and SAM systems.
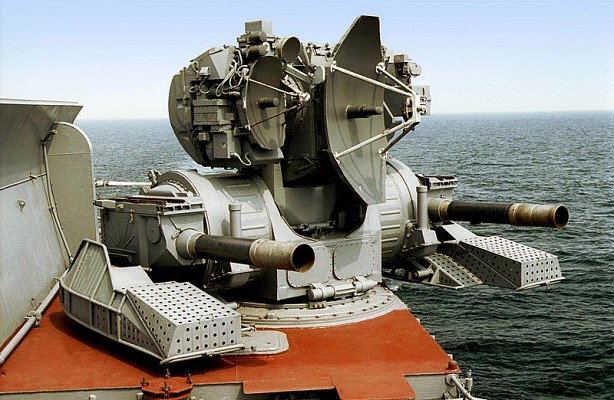

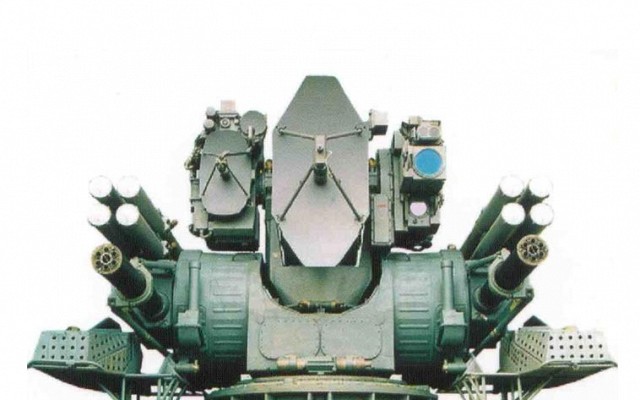
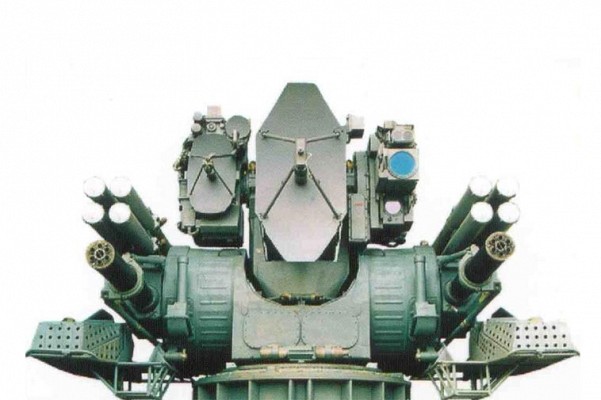
Kortik
Naval close-in weapon system with eight 9M311K missiles ready to fire.