SET-40
Overview
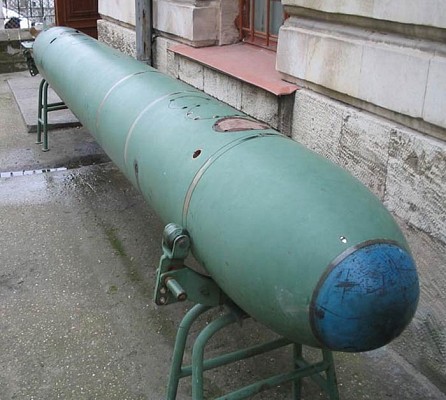

SET-40
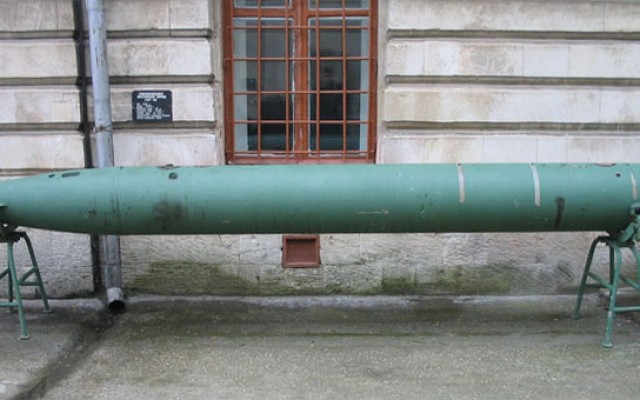
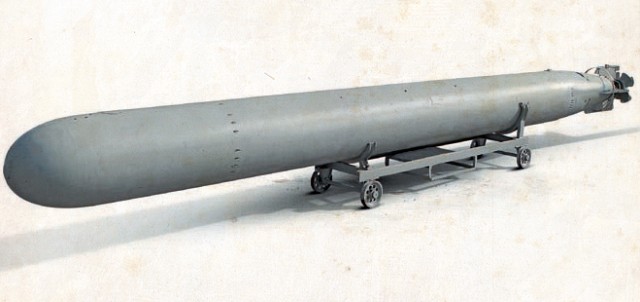
Forward view of SET-40 torpedo on display in a museum.
Source: wwww.militaryrussia.ru -
© Copyright lies with original owner
1968 for SET-40U
SET-40 / Spetsialnaya Elektricheskaya Torpeda 40
Russian for "special electric torpedo 40"
MGT-2
Type 40 (NATO classification)
Izdeliye 241 (article index)
Description
Introduction
The SET-40 is an early Cold War era lightweight torpedo of Soviet origin. It was developed to arm both submarines and small anti-submarine vessels with a lightweight torpedo for use against enemy submarines.
Design
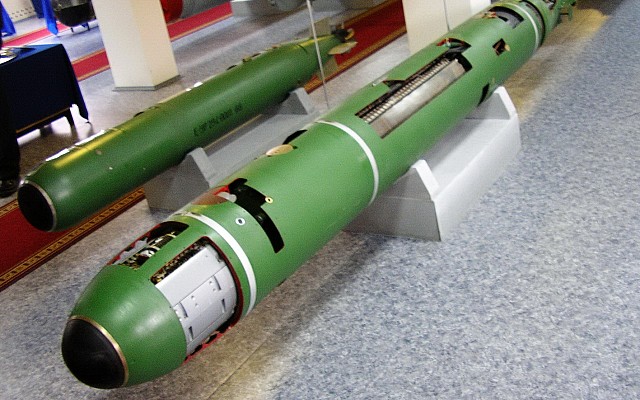
The SET-40 is designed to the same external parameters as the 400mm MGT-1 lightweight torpedo. Whereas the MGT-1 is to be used against small surface vessels, the SET-40 is for use against submarines. The SET-40 is divided into four compartments. These are the sensor, warhead, battery and engine compartments. The engine and battery design are derived from the much larger 533mm SET-53M torpedo. An electric motor drives the single propeller. The silver-zinc batteries are seawater activated, prohibiting use in fresh water environments.
Guidance
The SET-40 was the first torpedo in Soviet service with both active and passing homing. The SET-40 used a first generation acoustic sensor with 600 to 800 m range. The SET-40U has the more capable Sapfir sensor, which is partly derived from US technology.
Firepower
The SET-40 has a range of about 8 km while travelling at a speeds of up to 29 knots. The 80 kg warhead is set off by an acoustic proximity fuse. The SET-40U adds a contact fuse as back-up for the proximity fuse.
Launch platforms
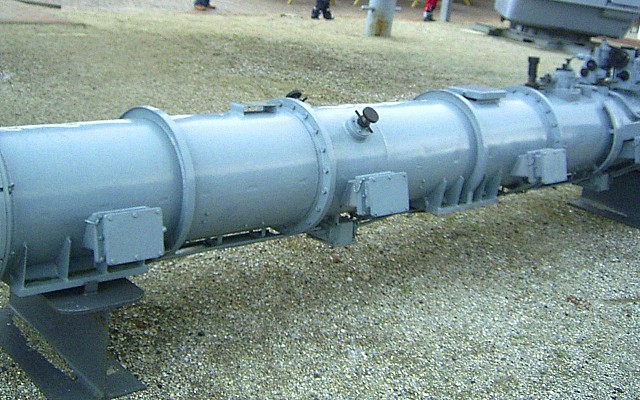
The SET-40 is one of the few types of lightweight torpedoes used on submarines. Several types of early to mid Cold War era Soviet submarines were fitted with 400 mm torpedo tubes. On surface vessels the SET-40 is launched from OTA-40 torpedo tubes. These are single deck mounted tubes, of which several can be fitted to small surface vessels. A powder charge launches the torpedo from the tube. The OTA-40 launch tube can be connected to a fire control system or (for export) use manual input.
Users
The main user of the SET-40 was the USSR. Unlike the MGT-1 the SET-40 proved to be a successful design. Large numbers were used on small anti-submarine vessels. Many nations with ties to the USSR acquired such vessels. The SET-72 was developed as a universal torpedo to replace the SET-40.
Variants
Details
Media
Related articles

MGT-1
The SET-40 was develop with the same dimensions as the MGT-1. Whereas the SET-40 is for use against submarines, the MGT-1 is intended to engage surface vessels.
SET-53
The SET-40 has some design elements that are derived from the much larger SET-53 torpedo, most notable the SET-53M which was developed at the same time.





